A new queen bee will hatch from an identically same egg as a worker bee. The only difference is the food with which the larva is fed.
The egg
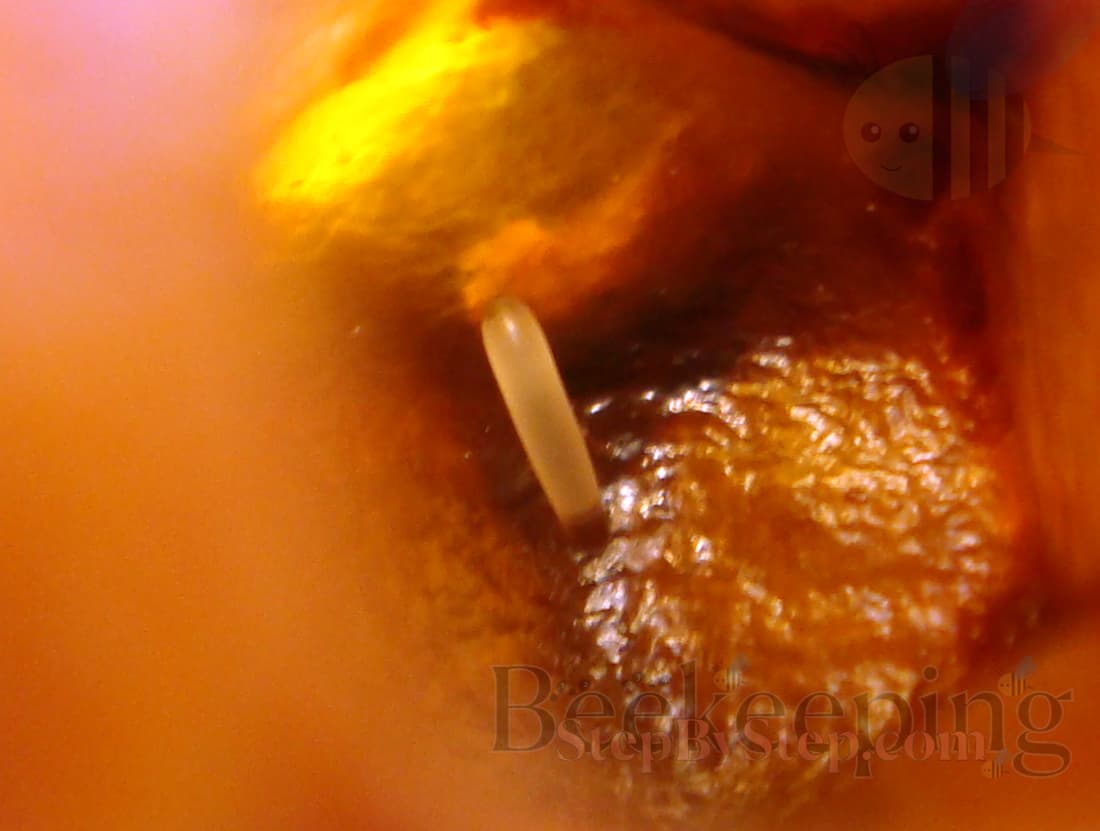
In order for a young queen to develop, another queen bee needs to lay a fertilized egg.
In 3 days a larva will hatch from the egg. Whether a queen bee or a worker bee develops from that larva, depends on the colony’s needs (the food the bees feed the larva).
Advertisement :

Beekeeping for Beginners
Everything you need to know!
This is a full beekeeping course for beginners.
Queen larva
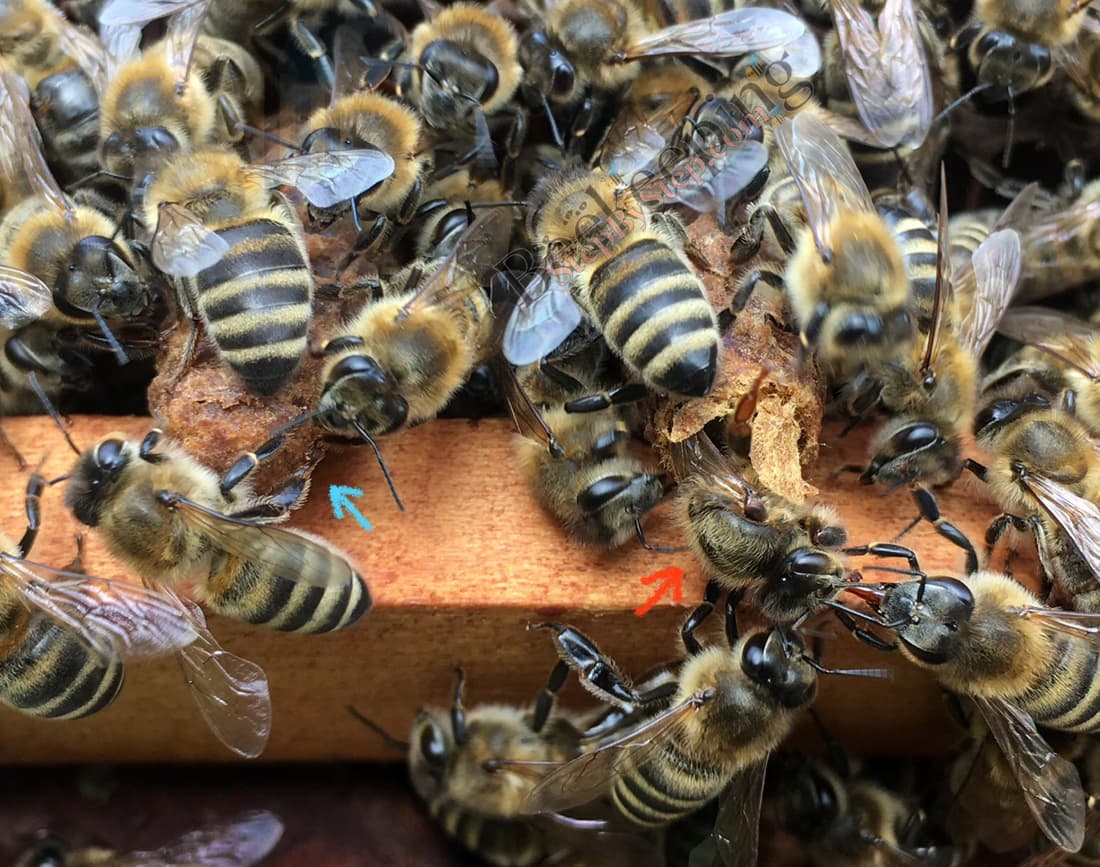
If the colony needs to make a new queen, worker bees pay special attention to chosen larvae and feed them abudantly with royal jelly only.
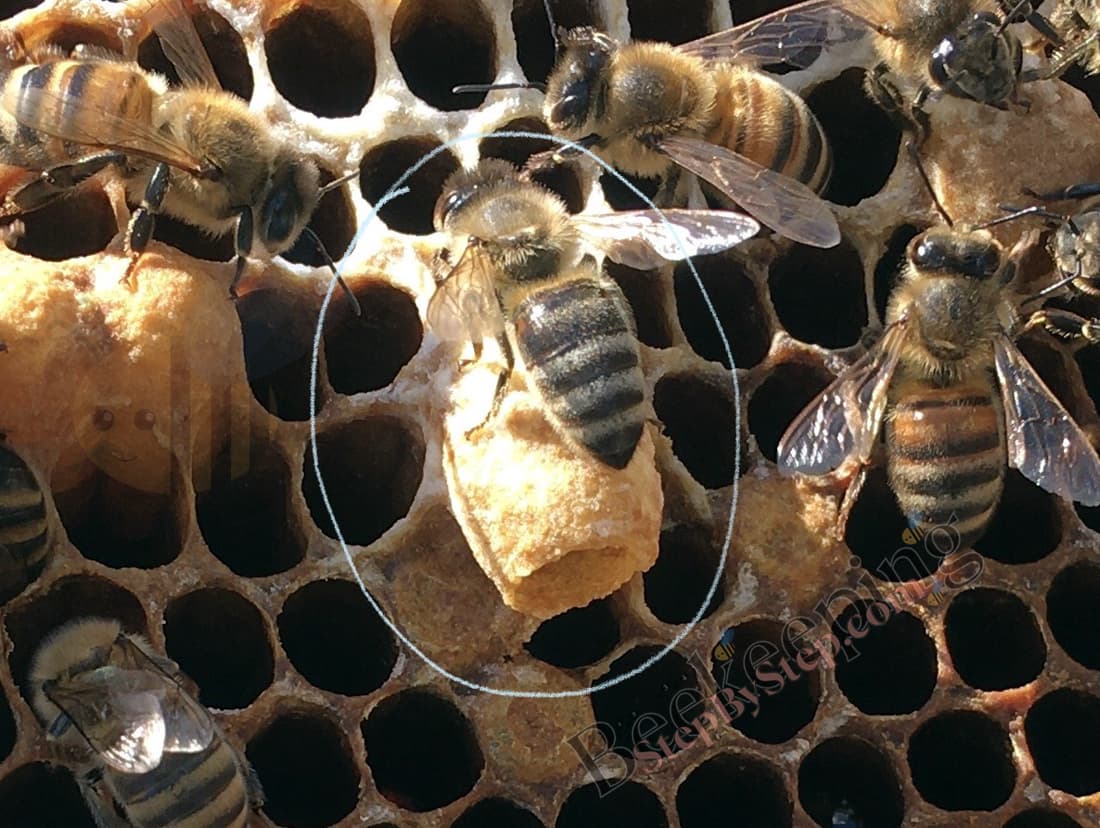
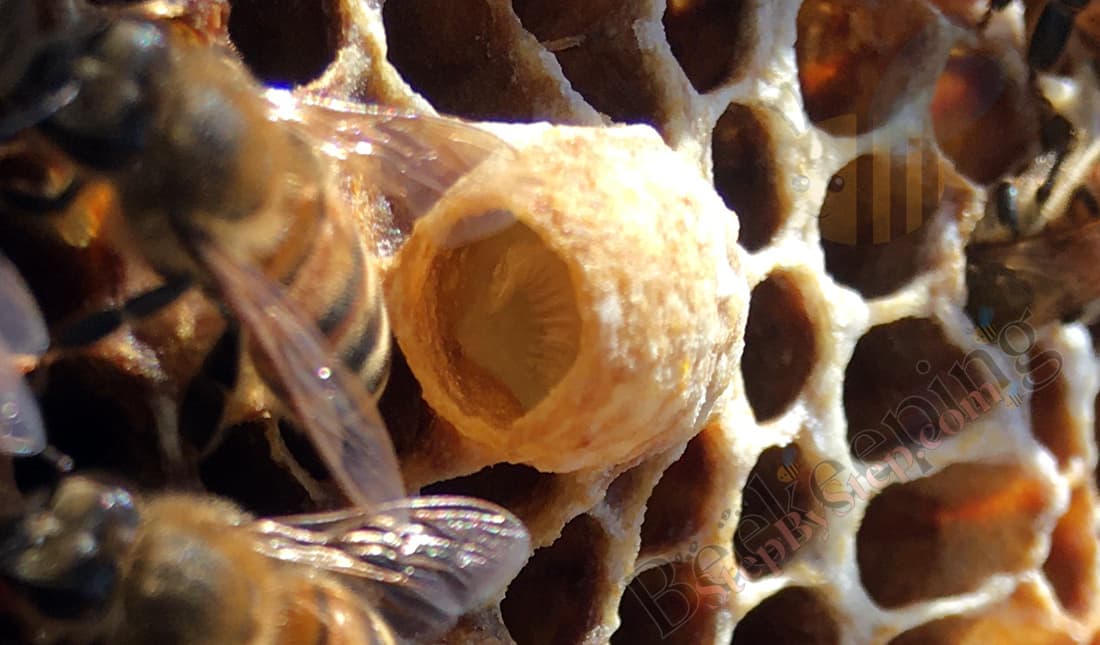


The bees can start making a large number of queens at the same time by choosing a number of larvae that are up to 3 days old and start filling their cells with large quantities of royal jelly which the larvae eat.
A new queen is 5.5 days in larva stage.
Bees are feeding queen larva exclusively with great quantities of royal jelly all the time until they close her cell.
Queen cell is a cell in which a new queen bee develops.
Queen pupa
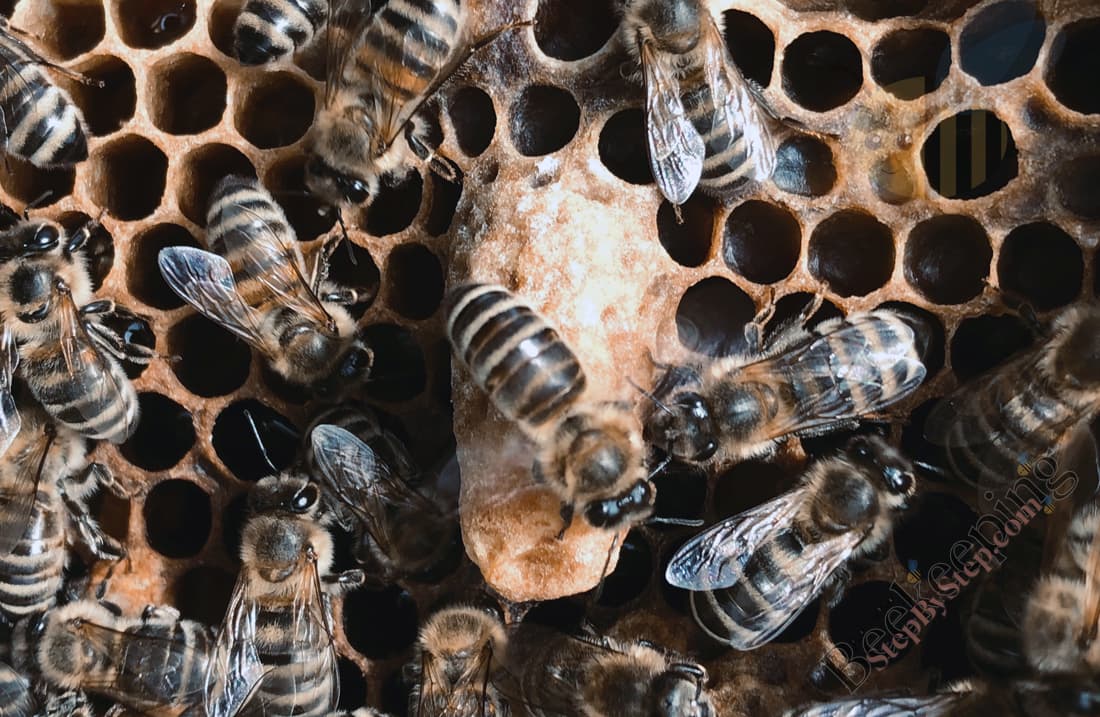

A new queen spends 7.5 days in pupa stage.
16 days after the egg was laid, young unmated queen bee chews through the top of the queen cell and comes out.

Unmated queen bee
Unmated queen is little bit smaller than a mated. She is not much bigger than the workers, so it is harder to spot her among worker bees.
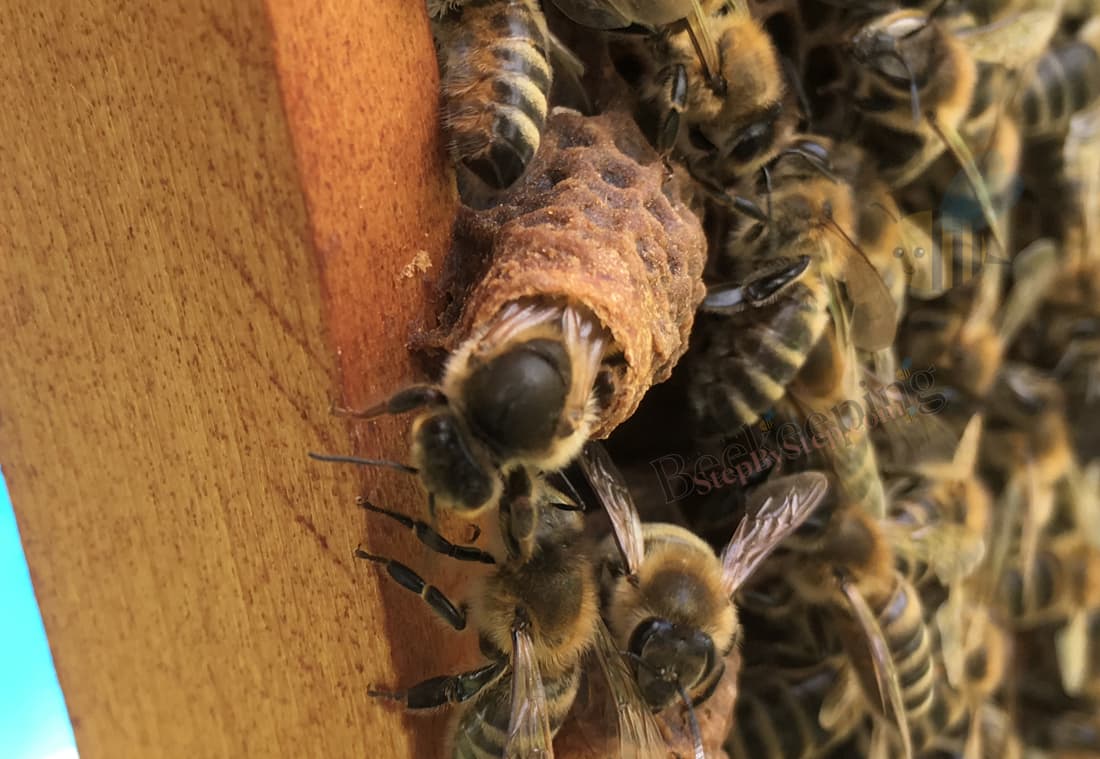


It is possible that there is a big number of unmated queens in a colony.
If the bees allow it, the first queen that comes out of her queen cell can destroy other queen cells. During the swarming, the bees protect the queen cells that need to emerge, from already emerged queens.
If the queen meets another queen, there will be a fight and one of them will be killed.

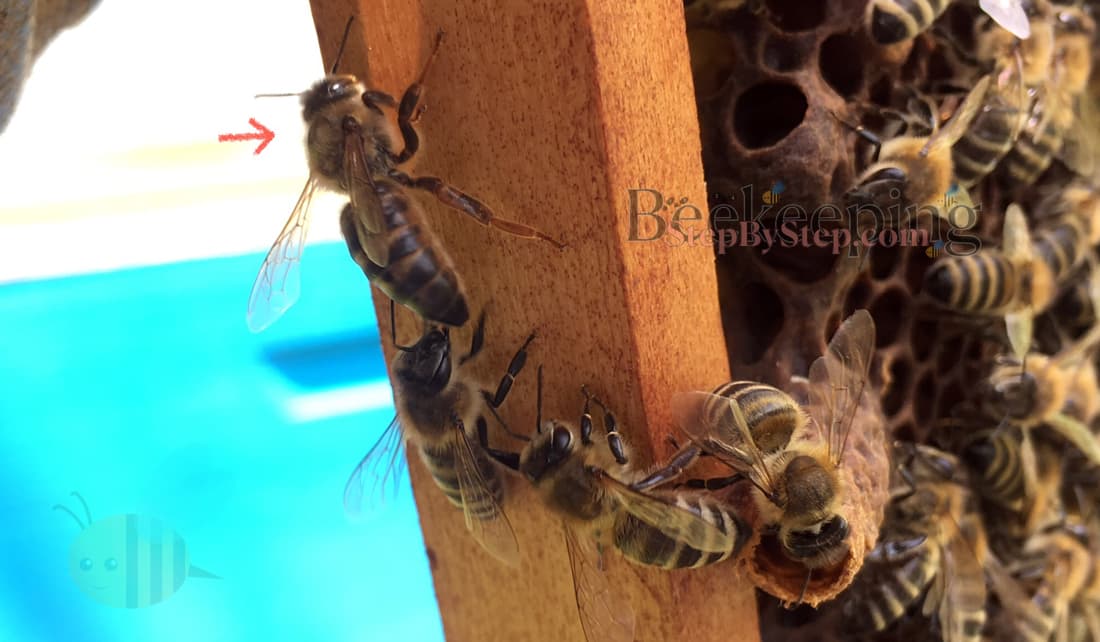
Young, unmated queen bee is nervous, running along the honeycomb and can be easily frightened so the beehive which has an unmated queen should not be opened because she can fly off the frame.
If the unmated queen flies off the frame, the frame should be held in the same position for a few minutes so she can come back.
Nuptial flight
In order for the queen bee to lay fertilized eggs from which the worker bees will hatch, she needs to mate with a drone. While mating, the queen will receive an amount of spermatozoids which will fertilize the eggs for few years.
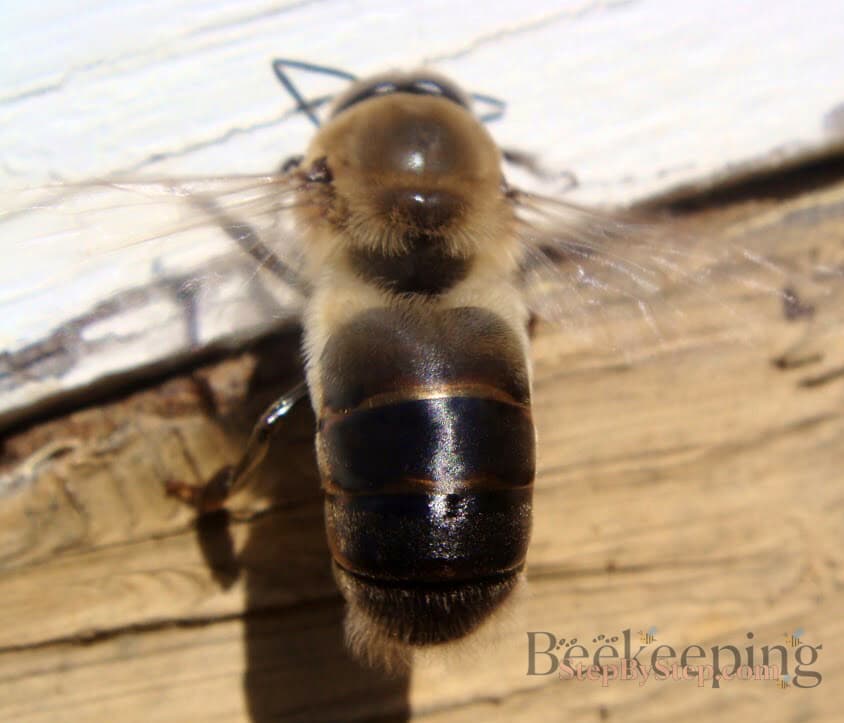

The queen mates while flying, with a few drones which die afterwards. This is called a nuptial flight.
The queen goes on several nuptial flights until she starts laying eggs. But when she starts laying eggs she doesn't leave the beehive except when swarming starts.
The queen bee usually goes on her nuptial flight 6-7 days after leaving her queen cell.
If she doesn't mate after 20 days, she starts to lay unfertilized eggs from which only drones will hatch. That kind of queen is called a drone laying queen.
Mated queen bee
Only one queen will mate and start laying eggs.
Mated queen starts laying eggs 2-5 days after mating.
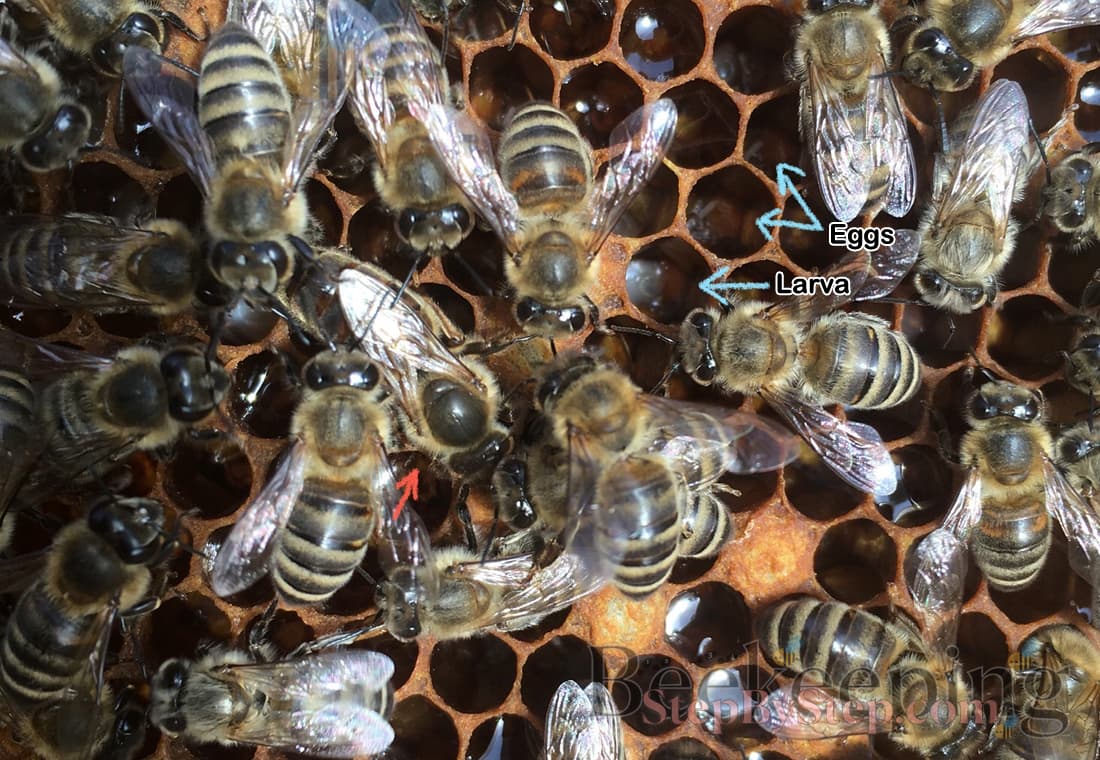

Experienced beekeeper can spot polished honeycomb cells which the bees prepare for laying eggs, which means the young queen has mated and will soon start laying eggs.
The queen lays one egg in one cell but sometimes a young queen can lay 2 or 3 eggs in one cell in the beginning. If the queen is healthy this will normalize and after 5-8 days she will lay one egg in one cell.
Mated queen is bigger than unmated queen, but whether the queen is mated or not can be concluded with certainty only by the presence of the worker brood in the hive.